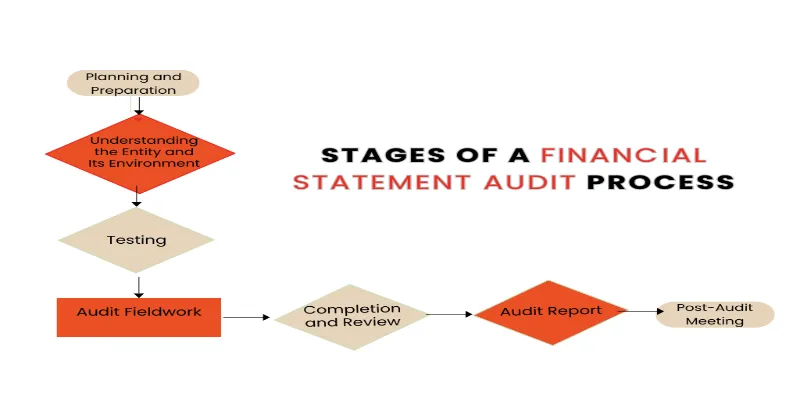
How To Become A Tax Filer In Pakistan ?

Tax filing in Pakistan involves declaring your income and expenses to the Federal Board of Revenue (FBR) to determine your tax liability. Anyone earning above the government’s minimum taxable limit, whether salaried employees, freelancers, or business owners, must file their sales tax returns annually. Becoming a tax filer isn’t just a responsibility—it’s an intelligent choice that brings numerous benefits. , like better loan options and lower withholding taxes. Although the process might seem very tricky, proper guidance can simplify it! Understanding and following the steps to file taxes correctly can significantly smooth out your financial path.
Let’s break down the steps to make tax filing in Pakistan as easy as possible.
Documents Required For Filers & Updates Of Tax Calendar
When preparing to file your taxes in Pakistan, organising your documents and understanding the tax calendar is crucial. Gathering all necessary documents beforehand is essential to ensure a smooth tax filing process. Here’s a checklist:
- CNIC (Computerised National Identity Card): Your official identification number is required for all tax-related activities.
- Proof of Income: This includes salary slips for salaried individuals, freelancer income statements, and business financial statements.
- Statements: These are typically required for the fiscal year to verify your financial transactions.
- Proof of Tax Deductions and Credits: This includes receipts for charitable donations, proof of investment, and educational expenses.
- Information on Dependents: CNICs of dependents and proof of their expenses, if applicable.
- Property and Asset Details: Documentation related to owned properties and other assets.
It’s helpful to maintain these documents in digital and physical formats to facilitate easy submission during the filing process.
Understanding The Tax Calendar
Awareness of critical dates and deadlines in the tax calendar is essential to avoid penalties and maximise potential rebates. Here’s a basic outline of the tax year in Pakistan:
| Event | Date/Deadline |
|---|---|
| Tax Year Start | July 1 |
| Filing of Tax Returns Deadline | September 30 |
| Last Date for Revised Returns | December 31 |
Please note that these dates can vary, especially under exceptional circumstances or extensions announced by the FBR. Always check the FBR website or reliable financial news sources for current information.
Step-by-Step Process To Register As A Tax Filer
Becoming a tax filer in Pakistan involves registering with the Federal Board of Revenue (FBR) and subsequently filing your tax returns through their online system, IRIS. Here’s an easy, step-by-step guide to navigate this process smoothly:
Step 1: Register as a Filer with FBR
- Visit the FBR Website, open your web browser, and go to the FBR website.
- Click on ‘Income Tax’ or ‘IRIS’ under the Online Services section.
- Choose between ‘Income Tax Return Filing for users within Pakistan’ and users outside Pakistan.
- Click on “Registration for Unregistered Person”.
- Enter all required details such as name, CNIC, and contact information, and then click ‘Submit.’
- You will receive a verification code via SMS and email. Enter these codes where prompted on the website.
- Upon successful verification, you will receive your login credentials via SMS and email.

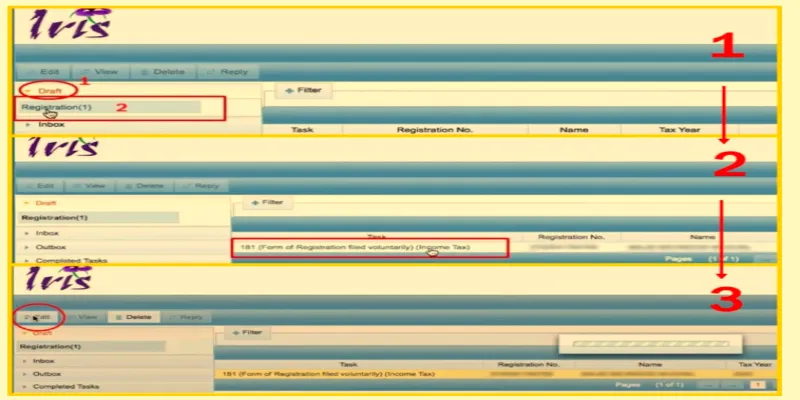
Step 2: Complete Your Registration in IRIS
- Go to the IRIS login page, and enter your CNIC (without dashes) and the received password.
- Navigate to the Drafts: Click on the ‘Draft’ button, then select ‘Registration’.
- Form 181: Click on ‘Form 181’ to open the registration form.
- Fill the Form: Auto-filled personal details will appear. Add addresses in the ‘Property’ section and link your employer in the ‘Link’ tab.
- For addresses, click the + sign, enter the details, and confirm.
- In the ‘Link’ tab, select ‘Employer’, search for your employer’s name, and add job details like start date and share (usually 100%).
- Save and Submit: Frequently save your progress using the ‘Save’button. Once all details are verified, click ‘Submit’ to finalise your registration.
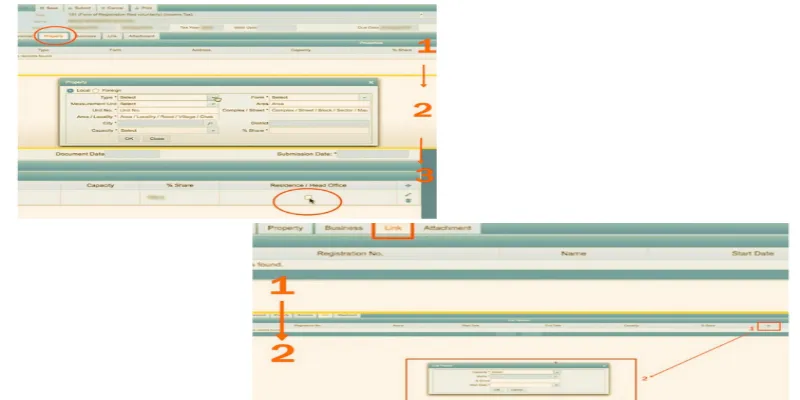
Step 3: File Your Income Tax Returns
- Once registered, log in again to IRIS.
- Click on the ‘Declaration’ tab, then choose the appropriate option for your income sources.
- Input Your Financial Details:
- Enter your annual salary and any tax-exempt components.
- Add details of other income sources and calculate the tax.
- If applicable, add income from foreign sources.
- Agricultural Income: Add details if you have income from agriculture.
- Tax Deductions and Payments:
- Add any tax deductions applicable to your profession or investments.
- Enter details of any taxes already paid, such as advance tax or tax on financial transactions.
- After entering all details, use the ‘Calculate’ button to see the tax due or refundable.
- Review all entries, and if satisfied, click ‘Submit’ to file your tax return.
This detailed guide simplifies the process of becoming a tax filer in Pakistan, ensuring you can handle it independently and efficiently. Remember, keeping your documents organised and following each step carefully will make the process smoother. If you encounter difficulties, FBR’s helpline and online services like tax consultants are available to guide you.
What Next After Submission?
Once you have successfully submitted your tax returns, your next goal is to secure your position on the Active Taxpayer List (ATL). Your name will typically appear on the ATL within a few days after your return is processed. Being on the ATL confers significant advantages, such as reduced tax rates on bank transactions and lower withholding taxes on various transactions, enhancing your financial dealings throughout the year.New filers often encounter challenges such as submission errors or delays in appearing on the ATL. If you face such issues, the first step is to verify that all submitted information is accurate and complete. For unresolved issues, the FBR helpline is an essential resource, offering guidance and solutions. Additionally, consulting with a tax advisor at “Khan & Co” can provide professional assistance and help navigate complex tax matters effectively. Remember, timely resolution of filing issues ensures that you maintain good standing as a tax filer and can fully benefit from your taxpayer status.
Benefits of Becoming a Tax Filer in Pakistan
In Pakistan, registering as a tax filer offers a multitude of financial advantages that can significantly impact your economic activities positively. Here are some compelling reasons why you should consider becoming a registered filer:
- As a registered filer, the tax deducted on profits and income tax withdrawals from banks is significantly lower than that for non-filers, ensuring you retain more of your earned interest and savings.
- When buying or selling property, registered filers benefit from a reduced tax rate, which can lead to substantial savings in large transactions.
- Selling securities? As a filer, you’ll enjoy a lower withholding tax rate on the capital gains compared to non-filers, making investing in stocks and bonds more profitable.
- Registering and transferring motor vehicles come with a reduced withholding tax for filers. This reduction can lessen the financial burden associated with vehicle ownership changes.
- Receive dividends? Filers pay a lower tax rate on dividends than non-filers, increasing your net investment income.
- Winning a prize bond can be more fruitful as a filer, thanks to lower withholding taxes compared to what non-filers have to pay.
- One of the most practical benefits of being a filer is the ability to claim a refund on overpaid taxes directly from the FBR, providing an opportunity to recover funds that may have been excessively deducted throughout the year.
These benefits highlight the financial incentives provided by the Pakistani government to encourage tax registration and compliance, aiming to broaden the tax base while rewarding those who participate actively in the tax system.
Wrapping Lines!
Becoming a tax filer in Pakistan is a strategic decision that brings considerable personal and financial benefits. By following the outlined steps, you can experience a smooth and advantageous tax filing process. Start early to manage each step efficiently and avoid complications. If you encounter challenges, seeking professional advice by tax consultants is highly recommended. For more assistance or to connect with tax professionals, contact us directly. Begin your tax filer journey today and take charge of your financial obligations in Pakistan.