Types of Taxes in Pakistan

In Pakistan, the taxation system is classified into two basic categories; direct taxes and indirect taxes. This system is very complex. There are more than 70 different types of taxes that are administered by roughly 37 different organizations. The following is a general explanation of how these taxes are administered:
- Direct Taxes
- Indirect Taxes
Taxes are classified into direct taxes and Indirect Taxes In Pakistan as;
| Sr | Direct Taxes | Indirect Taxes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Income tax | Sales tax |
| 2 | Property tax | Value added tax |
| 3 | Capital gain tax | Excise duty |
| 4 | Custom duty |
Direct Taxes
This tax is imposed directly on the earnings or profits of the payer rather than on the purchase of goods and services. Typically, direct taxes are charged according to the ability-to-pay premise. We can say that redistributing the nation’s wealth inside its borders is the fundamental or primary goal of direct taxation. Unlike indirect taxes, which are passed on to different people or organizations, direct taxes are not. Direct taxes are progressive by nature as they reproduce wealth. These taxes collect 25% of tax revenue. These taxes are paid directly to the governing entity.
These taxes include;
- Salaries
- Property Income
- Income on security
- Business Income
Types Of Direct Taxes
To calculate total income and charge taxes, further classification is necessary. Direct taxes are thus classified as;
- Income tax
- Property tax
- Capital Gain Tax
1. Income Tax
Following certain allowances, income tax is levied on all earnings obtained by private individuals. Income tax is a significant source of government revenue in the majority of economies.
It depends on a person’s income. Depending on how much a worker makes, a set proportion of his or her pay is withheld. The government is anxious to include credits and deductions that assist people to reduce their tax obligations, which is a good thing.
2. Property Tax
Any resident who owns immovable property in Pakistan is subject to presumed income tax. This deemed income will be calculated as 5% of the immovable property’s fair market value and such income is subject to a 20% specified tax rate. It is a tax based on the property’s worth that the owner must pay. To sustain public services property tax is levied on assets.
3. Capital Gain Tax
The profit made from the sale of a non-inventory asset that was acquired for less is subject to capital gains tax. The selling of stocks, bonds, precious metals, and real estate results in the most frequent types of capital gains. Not all nations impose a capital gains tax, and the majority have various rates of taxation for both individuals and businesses. This tax is calculated by finding the difference between the acquisition amount and the selling amount.
Indirect Taxes
This is a sort of tax that is incurred indirectly by the taxpayer. Taxes like these are transferred from one taxpayer to another. It is imposed on products and services, thereby raising the cost of those items. In contrast to direct taxes, indirect taxes are often imposed on all taxpayers equally, regardless of their wealth. Because all taxpayers, rich and poor, must pay the same amount in taxes on goods and services, indirect taxes are viewed as regressive. In Pakistan, indirect taxes make up the majority of government income. Please read the fundamental distinctions between direct taxes and indirect taxes listed below for additional information. These taxes collect 75% of tax revenue.
This tax includes:
- Sales Tax
Types Of Indirect Taxes
Like direct taxes, indirect taxes are also further classified:
- Sales Tax
- Value Added Tax
- Excise Duty
- Custom duty
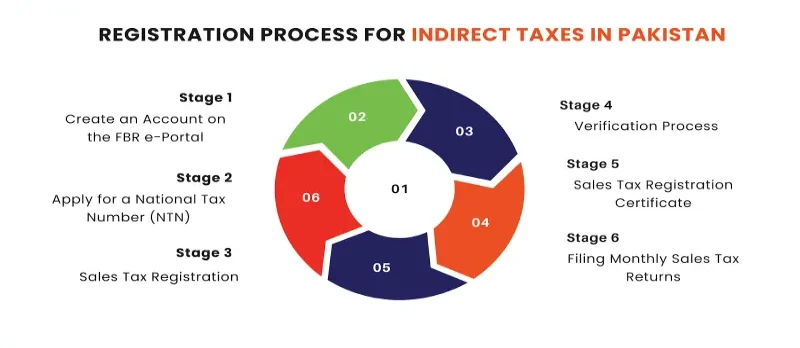
1. Sales Tax
A sales tax is one of the most prevalent indirect taxes. Everything is subject to sales taxes, including groceries, fast food, gadgets, and apparel. The city, county, or state where the transaction is made has different sales taxes.
2. Value-Added Tax
When a product moves through numerous manufacturing or production chain stages, this tax is imposed on products. The product should first be provided through a supply chain, then it should get through production, and finally, it should get to stores or markets for sales. Each stage receives a percentage of the tax applied.
3. Excise Duty
Controls over the production and distribution of excisable goods, like alcoholic beverages and illegal substances, are the responsibility of the Excise Wing of the Taxation Department.
4. Custom Duty
When any commodity or service is imported from abroad, the government is subject to a certain form of duty known as customs duty. This is often paid in Pakistan at the time of customs clearance.
Direct Taxes Vs. Indirect Taxes
Direct and indirect taxes vary from eachother to a great extent. Their major differences are as follows:
| Sr | Direct Taxes | Indirect Taxes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Paid by an individual directly to the government | Can be transferred to another entity. |
| 2 | Reduce inflation | Increase inflation |
| 3 | Progressive | Regressive |
| 4 | Collected from assesses | Collected from consumer |
| 5 | Tax can be avoided by hiding income | Cannot be avoided as they cannot be hidden |
| 6 | Not levied equally | Tax Levied equally upon all taxpayers |
This article provides basic information about the types of taxes which is very essential to know. We hope it helps you better aware of the taxation system and creates convenience in filing your tax.
There are basically two types of taxes – direct and indirect taxes. The following are the differences between the two:
- Direct taxes refer to taxes that are filed and paid by an individual directly to the government. Indirect taxes, on the other hand, are taxes that can be transferred to another entity. Therefore, the burden of paying them can be put on another person’s shoulders.
- Direct taxes can be evaded in the absence of proper collection administration. Indirect taxes cannot be escaped from because these are charged automatically on goods and services.
- Direct taxes can help address inflation while indirect taxes can lead to inflation.
- Direct taxes lessen the savings of earners, but indirect taxes encourage the opposite because they make products and services more expensive and unaffordable.
- Direct taxes are imposed only on people that belong to various income brackets. Indirect taxes, on the other, can be felt by everyone who buys goods and avails services.